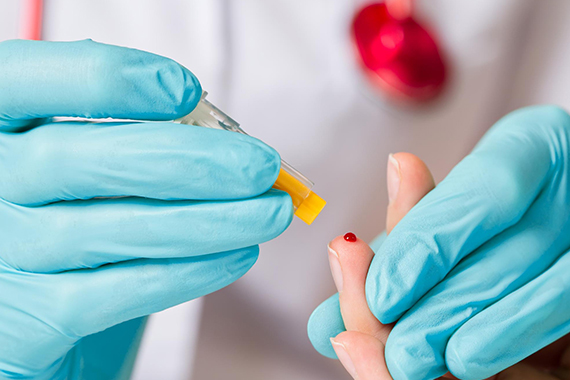
Rapid Vitamin D Blood Test in Great Yarmouth
Almost 1 in 5 UK adults has a low vitamin D status. Discover your vitamin D status quickly and conveniently with our in-pharmacy rapid test.
This test is available for £40 at Pharmacy Exprezz (NR30 1LS).

Benefits of Monitoring Your Vitamin D Levels
Early Deficiency Detection
Detect and treat deficiencies
Strong Immune System
Improves your body's defences
Vital for Bone Health
Vitamin D is vital for healthy bones
Improved Mood
Improve mood with optimal vitamin D levels
Harley Diagnostics
What Are the Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency?
1
General fatigue and tiredness
2
Frequent illness
3
Bone loss
4
Mood changes
5
Bone and muscle pain
6
Hair loss
How it works
How Does the Rapid Vitamin D Test Work in Great Yarmouth?
Our rapid test is a simple and efficient way to check your vitamin D levels. The process involves a quick and easy finger-prick blood test.
- A small blood sample is collected and applied to a special test card.
- The test card is inserted into an analysis machine.
- Results are provided within 15 minutes, right at the pharmacy.
- The clinic can also give you advice on supplements or signpost you to your GP, if required

Overview
What does the test look for?
Harley Diagnostics
Step-by-Step Guide to Your Visit at Pharmacy Exprezz.
1
Consultation
2
Blood Collection
3
Rapid Analysis
4
Results
5
Advice
Harley Diagnostic
What do your vitamin D test results mean?
The test results are provided on the test report in both nanomoles per litre (nmol/L) and nanograms per millilitre (ng/mL) measurements.
When you get your test results, your vitamin D levels will be shown in two measurements: nanomoles per litre (nmol/L) and nanograms per millilitre (ng/mL). The following table shows what your results mean and indicate.
| Vitamin D Level (nmol/L) | Vitamin D Level (ng/mL) | What do your results indicate? | When should I retest? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 25 nmol/L | Less than 10 ng/mL |
Deficient 25(OH)D levels below 25 nmol/L indicate Vitamin D deficiency risk. Consult your doctor or healthcare professional for supplementation advice. |
If you start to take supplements and make diet and lifestyle changes, you may retest in 3–6 months to find out if your levels have improved. |
| 25 to 50 nmol/L | 10 to 20 ng/mL |
Insufficient 25(OH)D levels between 25–50 nmol/L are insufficient/suboptimal. Speak with your healthcare professional for advice on supplementation and lifestyle changes. |
If you start to take supplements and make diet and lifestyle changes, you may retest in 3–6 months to find out if your levels have improved. |
| 50 to 75 nmol/L | 20 to 30 ng/mL |
Adequate Vitamin D levels between 50–75 nmol/L are adequate. Discuss with your healthcare professional for advice on supplements and lifestyle changes to achieve the optimal level. |
If you start to take supplements and make diet and lifestyle changes, you may retest in 6–12 months to find out if your levels have improved. |
| Above 75 nmol/L | Above 30 ng/mL |
Optimal Vitamin D levels above 75 nmol/L are optimal. Maintain current intake and healthy lifestyle. Caution: Levels above 250 nmol/L pose a toxicity risk. |
You may retest annually to monitor your vitamin D levels. |
Please be aware that different laboratories, manufacturers, and providers may use slightly different reference ranges. The reference ranges provided on this page are for general guidance only and represent commonly accepted clinical thresholds.
This rapid blood test is designed solely as an initial screening tool for triage and is not a substitute for a full lab-based venous blood draw. The results offer quantitative insights but are for informational purposes only and should not be considered a medical diagnosis. Any abnormal or significant result must be followed up with a medical assessment with your doctor and potential confirmatory lab-based testing.
Harley Diagnostic
Other Available Rapid Blood Tests
HELP & SUPPORT
Check Out Our Frequently Asked Questions!
What is Vitamin D?
What steps can be taken if you are found to be deficient in Vitamin D?
- Dietary changes: Incorporating foods rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), egg yolks, and fortified foods like cereals and milk.
- Lifestyle advice: Spending more time in the sun to help your body naturally produce vitamin D whilst following sun safety precautions.
- Supplementation: Taking a daily vitamin D supplement. Your healthcare provider can recommend a suitable dosage and type (D2 or D3). It is important to follow the advice of a healthcare professional and not to self-medicate.


.png)